AWS S3 파일 업로드,다운로드
👀 개요
이전 포스팅에서 S3에 대해서 간단하게 다뤘었다.
요번에는 S3에 파일을 올리는 과정을 포스팅하려 한다.
❗ S3에 대해서는 이전 포스팅 참고 S3란?
🦺 S3 버킷 생성에 대해서는 이전 포스팅 참고 S3 버킷 생성
🗑 S3 파일 업로드
- 버킷 생성
일단 나는 아래 그림처럼 file-upload-test-lee라는 명칭으로 퍼블릭한 버킷을 하나 생성했다.
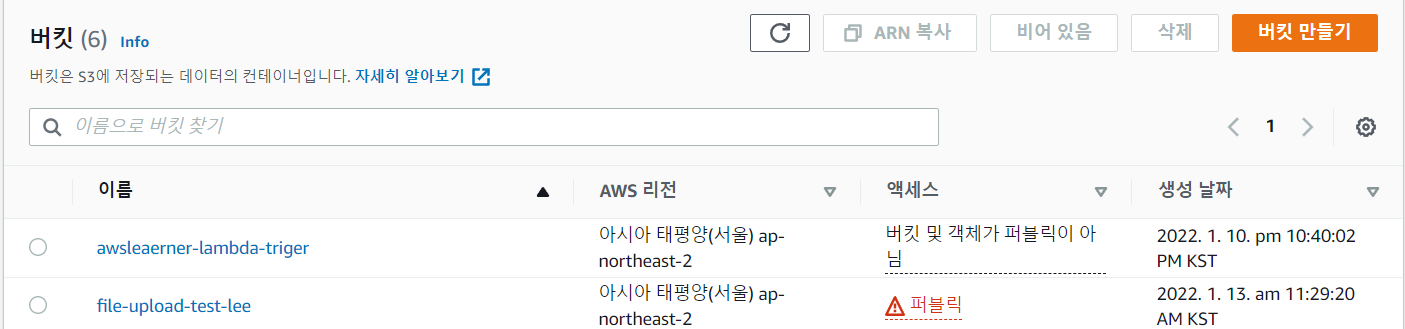
해당 버킷을 클릭하여 들어가면 아무런 객체도 없는 상태이다.
그리고 iam 권한에 사용자에게 S3 FullAccess 권한을 부여해야 합니다. (이것이 있어야 S3에 파일 업로드를 할 수 있습니다.)
일단 aws 상에서의 작업은 이 정도만 해주면 된다.
이제 실제 애플리케이션에서 aws s3 서비스를 구현해 보자.
- AmazonS3ClientBuilder 를 사용한 업로드 구현
의존성 추가
implementation group: 'org.springframework.cloud', name: 'spring-cloud-starter-aws', version: '2.2.5.RELEASE'프로젝트 구조
common
ㄴconfig
ㄴAmazonS3Config
controller
ㄴCheckController
aws
ㄴAwsSecret
ㄴSecretManagerBuild
service
ㄴS3Service
resources
ㄴapplication.yml
ㄴstatic.image.test
ㄴmey.jpg - AmazonS3Config
- CheckController
- AwsSecret
- SecretManagerBuild
- S3Service
- application
- mey.jpg: 로컬 테스트용 이미지파일을 넣어줬다.
먼저 나는 s3에 접근하기 위해 필요한 사용자의 정보를 secretmanager를 통해 받아올 것이기 때문에 위와 같이 구조를 만들어 주었다.
해당 부분에 대해서는 이전 포스팅을 참고 하자.
application.yml
secret:
name:
#_dev arn
key: #시크릿 매니저 arn
crawler: #시크릿 매니저 arn
ecm: #시크릿 매니저 arn
cloud:
aws:
region:
static: ap-northeast-2
stack:
auto: false
s3:
bucket: file-upload-test-leeapplication.yml 에 aws 관련 정보를 기재해 준다.
AmazonS3Config
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class AmazonS3Config {
/**
* aws 가용 지역
*/
@Value("${cloud.aws.region.static}")
private String region;
/**
* secretmanager key arn
*/
@Value("${secret.name.key}")
private String secretName;
/**
* s3 접근을 위한 위한 사용자 bean
*/
@Bean
public AmazonS3Client amazonS3Client() {
log.info("------------------------------------->AmazonS3Client");
AwsSecret secretKeys = SecretManagerBuild.getSecret(secretName,region);
String accessKey = secretKeys.getAws_ac_key();
String secretKey = secretKeys.getAws_se_key();
BasicAWSCredentials awsCreds = new BasicAWSCredentials(accessKey, secretKey);
return (AmazonS3Client) AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(region)
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(awsCreds))
.build();
}
}AmazonS3ClientBuilder 를통해 접근 정보를 만들어 준다.
S3Service
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Component
public class S3Service {
/**
* s3 접근 정보
*/
private final AmazonS3Client amazonS3Client;
/**
* S3 버킷 명
*/
@Value("${cloud.aws.s3.bucket}")
public String bucket;
/**
* 객체 url을 읽어온다
* @param {string} bucket 버킷명
* @param {string} fileName 파일명
* @returns {string} imageUrl 이미지 url
*/
public String read(String fileName) {
String imageUrl = amazonS3Client.getUrl(bucket, fileName).toString();
return imageUrl;
}
/**
* S3 파일 업로드를 위한 경로 재정의
* @param {File} uploadFile 업로드할 파일
* @param {string} dirName 경로명
* @returns {string} uploadImageUrl
*/
public String uploadMultipart(MultipartFile multipartFile, String dirName) throws IOException {
File uploadFile = convert(multipartFile) // 파일 변환할 수 없으면 에러
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("error: MultipartFile -> File convert fail"));
return upload(uploadFile, dirName);
}
/**
* S3 파일 업로드를 위한 경로 재정의
* @param {File} uploadFile 업로드할 파일
* @param {string} dirName 경로명
* @returns {string} uploadImageUrl
*/
public String upload(File uploadFile, String dirName) {
String fileName = dirName + "/" + uploadFile.getName();
String uploadImageUrl = putS3(uploadFile, fileName);
removeNewFile(uploadFile);
return uploadImageUrl;
}
/**
* S3 업로드
* @param {File} uploadFile 업로드할 파일
* @param {string} fileName 파일명
* @returns {string} awsS3UrlName 업로드된 url
*/
private String putS3(File uploadFile, String fileName) {
amazonS3Client.putObject(new PutObjectRequest(bucket, fileName, uploadFile).withCannedAcl(CannedAccessControlList.PublicRead));
String awsS3UrlName = amazonS3Client.getUrl(bucket, fileName).toString();
return awsS3UrlName;
}
/**
* S3 다운로드
* @param {string} fileName 파일명
* @returns {S3Object} obj 객체
*/
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> download(String storedFileName) throws IOException{
S3Object o = amazonS3Client.getObject(new GetObjectRequest(bucket, storedFileName));
S3ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = o.getObjectContent();
byte[] bytes = IOUtils.toByteArray(objectInputStream);
String fileName = URLEncoder.encode(storedFileName, "UTF-8").replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM);
httpHeaders.setContentLength(bytes.length);
httpHeaders.setContentDispositionFormData("attachment", fileName);
return new ResponseEntity<>(bytes, httpHeaders, HttpStatus.OK);
}
// 로컬에 저장된 이미지 지우기
private void removeNewFile(File targetFile) {
if (targetFile.delete()) {
log.info("File delete success");
return;
}
log.info("File delete fail");
}
// 로컬에 파일 업로드 하기
private Optional<File> convert(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
File convertFile = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/" + file.getOriginalFilename());
if (convertFile.createNewFile()) { // 바로 위에서 지정한 경로에 File이 생성됨 (경로가 잘못되었다면 생성 불가능)
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(convertFile)) { // FileOutputStream 데이터를 파일에 바이트 스트림으로 저장하기 위함
fos.write(file.getBytes());
}
return Optional.of(convertFile);
}
return Optional.empty();
}
}S3에 접근 후 내가 필요한 작업들을 정의해준다.
CheckController
@RestController
public class CheckController {
@Autowired
private S3Service s3Service;
//multipartfile 업로드시
@GetMapping("/fileUpload")
public String check(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file){
try {
s3Service.uploadMultipart(file,"uploadTest");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK";
}
//서버에 저장되어 있는 파일 업로드시
@GetMapping("/localUpload")
public String fileUpload(){
try {
String fileName = "mey.jpg";
File file = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:static/image/test/"+fileName);
s3Service.upload(file,"uploadTest");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK";
}
//S3에 저장된 파일 다운로드
@GetMapping("/localDown")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> fileDownload() throws IOException{
return s3Service.download("uploadTest/mey.jpg");
}
}나는 두 가지 방식을 테스트하려 한다
첫 번째 resources 영역에 내가 미리 넣어둔 이미지 파일을 업로드하는 방식
두 번째 포스트 맨으로 multipartfile을 보내 업로드하는 방식
사실 둘 다 로컬에 한번 저장하는 과정이 필요하다 s3 service를 보면 더 자세히 알 수 있다.
- 포스트 맨을 통한 테스트
먼저 첫 번째 방식을 테스트해보자 아래와 같이 요청을 했을 때
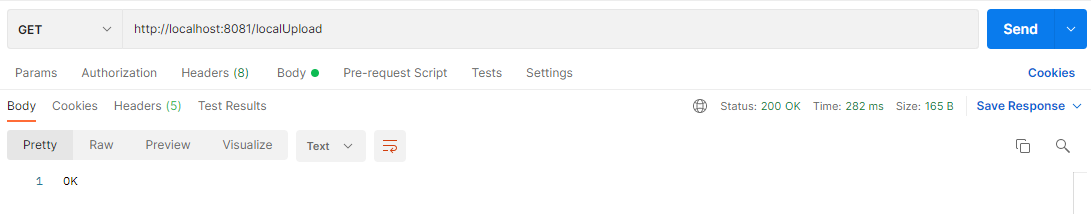
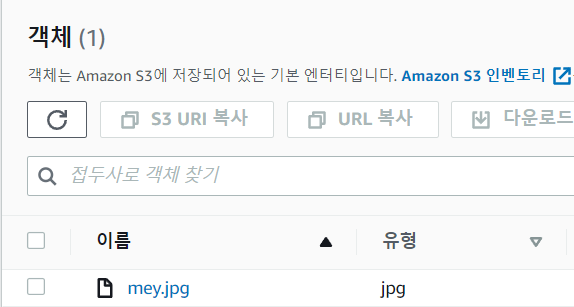
내가 생성한 버킷에 설정한 폴더명이 생기고 클릭해보면 로컬에 넣어놨던 파일이 저장되어 있다.
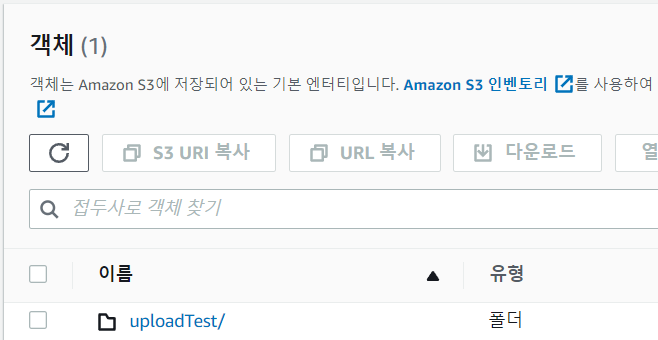
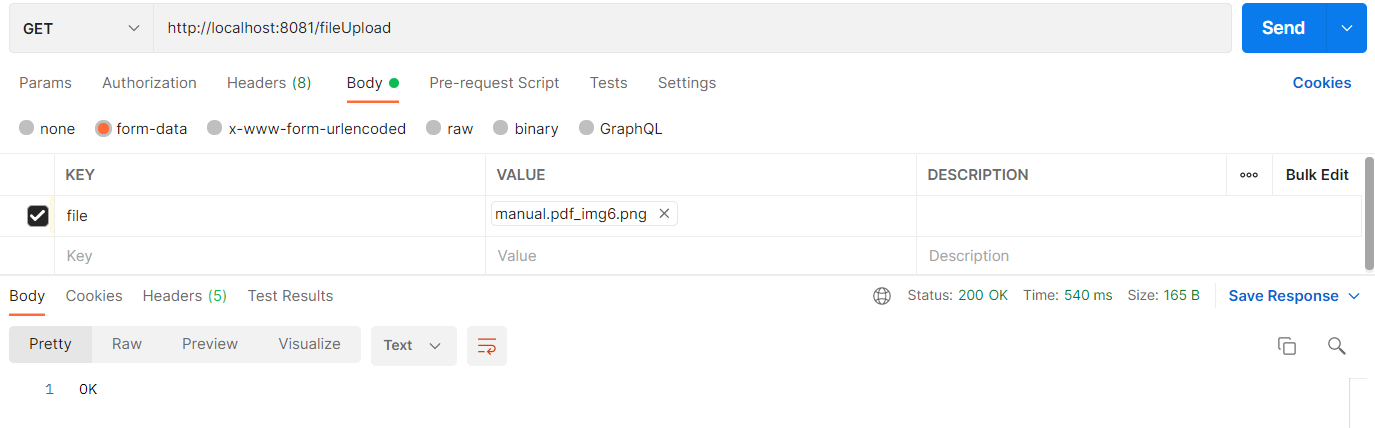
두 번째 방식도 테스트를 해보자
아래와 같이 파일을 넣어서 요청해 보면
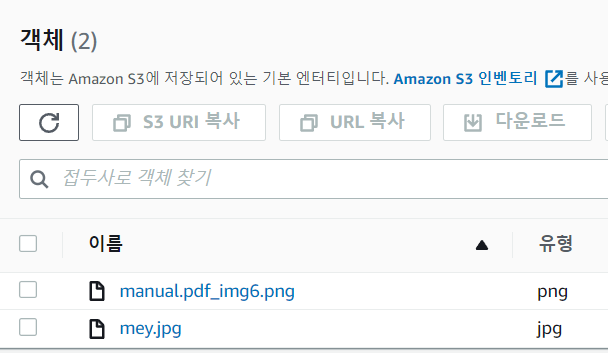
같은 버킷의 폴더에 아래와 같이 내가 보낸 파일이 업로드된 걸 볼 수 있다.
- S3 객체 다운로드 테스트
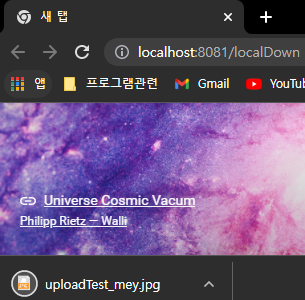
브라우저 창을 하나 열고 다운로드 테스트를 해보자
아래처럼 내가 방금 업로드한 파일이 잘 다운로드되는 걸 확인할 수 있다.
🌭마무리
이처럼 간단하게 springboot를 사용하여 s3에 접근 후 파일 업로드 다운로드를 구현해 보았다.
굉장히 간단한 예제이므로 공식문서 등을 참고하여 좀 더 여러 방식으로 사용이 가능하다 생각된다.